1
Application of biotechnology in agriculture
There are three options to increase the food production. They are
1. Agrochemical based agriculture
2. Organic agriculture
3. Genetically engineered crop based agriculture
Other applications of biotechnology in agriculture are
1. Cell and tissue culture
2. Somatic hybrids
3. Hybridisation through embryo rescue
4. Anther and pollen culture
5. Plant transformation
2
Gene therapy and its type
1. Gene therapy is the therapeutic delivery of nucleic acid polymers into a patient’s cells as a drug to treat disease.
2. Somatic gene therapy is the transfer of genes into the somatic cells of the patient, such as cells of the bone marrow, and hence the new DNA does not enter the eggs or sperm.
3. Germline gene therapy involves the modification of germ cells (gametes) that will pass the change on to the next generation.
4. With germline therapy genes could be corrected in the egg or the sperm that is being used to conceive.
3
Genetically engineered insulin
1. The gene for human insulin is inserted into a plasmid, this genetically modified plasmid is then inserted into E.coli. The genetically modified bacteria is then capable of the production of human insulin. This is called genetically engineered insulin.
4
Application of biotechnology in agriculture
There are three options to increase the food production. They are
1. Agrochemical based agriculture
2. Organic agriculture
3. Genetically engineered crop based agriculture
Other applications of biotechnology in agriculture are
1. Cell and tissue culture
2. Somatic hybrids
3. Hybridisation through embryo rescue
4. Anther and pollen culture
5. Plant transformation
5
Genetically modified organisms
1. A genetically modified organism (GMO) is any organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques (i.e., a genetically engineered organism). GMOs are the source of medicines and genetically modified foods and are widely used in scientific research and to produce other goods.
6
Transgenic organisms
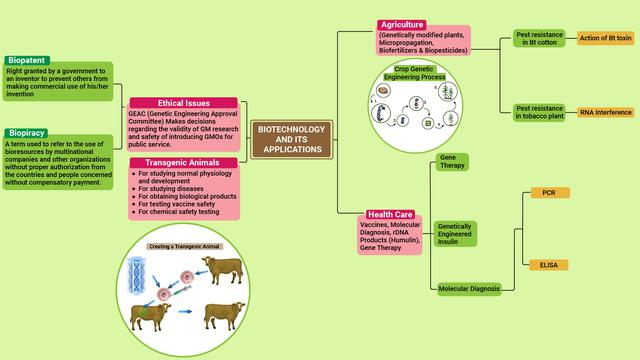
Some examples of transgenic plants and animals are as follows:
1. Transgenic plants: For example, tomatoes, Bt cotton, golden rice, corn, soybean, Bt brinjal.
2. Transgenic animals: For example, transgenic goats.
3. Transgenic bacteria: For example, mercury resistant bacteria.
7
Genetic transformation in plants
Genetic transformation in plants include the following four steps:
1. Introduction of foreign DNA into the plant cells
2. Integration and stabilization of foreign DNA in the cell nucleus or organelle
3. Regeneration of transformed cells or tissue into the whole new plant
4. Transmission of foreign genes in subsequent generation
8
Genetic transformation in animals
Some methods for transformation of the fertilized eggs are as follows:
1. Microinjection method
2. Replacement of nuclei
3. By cloning
9
Bt
1. Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is a spore forming bacterium that produces crystal protein (cry proteins), which are toxic to many species of insects.
2. Bt is largely used in agriculture, especially organic farming. Bt is also used in urban aerial spraying programs, and in transgenic crops.
10
Biopiracy
1. Some organisations and multinational companies exploit and/or patent biological resources or bioresources of other nations without proper authorisation from the countries concerned, this is called biopiracy.
11
Patent
1. Patent is the right granted by a government to an inventor to prevent others from commercial use of his invention.
12
Necessity of biopatent
1. Biopatent is a legal property offered by the state to the inventor by giving exclusive rights to make, use, exercise and vond the invention for a limited period.
2. Since, once product hit the market it can be easily duplicated by everyone. So in order to avoid duplication, patent protection is essential.