1
Introduction of carbon and its compounds
1. Carbon is an element with atomic number 6 with symbol C.
2. Carbon shows sp3 hybridization hence its valence is 4 and it is called tetravalent.
3. Carbon is most commonly obtained from coal deposits, although it usually must be processed into a form suitable for commercial use.
4. Three naturally occurring allotropes of carbon are known to exist: amorphous, graphite and diamond.
5. Carbon is present in saturated form, eg. Alkane, where it contains a single bond.
6. Carbon in unsaturation shows double and triple bond eg. Alkyne
2
Hyperconjugative strutures

content Text
3
Basic Rules of nomenclature of hydrocarbons
1. Identification of the parent hydrocarbon chain.
2. Identification of the parent functional group, if any, with the highest order of precedence.
3. Identification of the side-chains.
4. Identification of the remaining functional groups, if any, and naming them by their ionic prefixes.
5. Identification of double/triple bonds.
6. Numbering of the chain.
7. Numbering of the various substituents and bonds with their locants.
Examples : CH3CH2CH2OH = 1-Propanol
4
Nomenclature of simple aromatic compounds
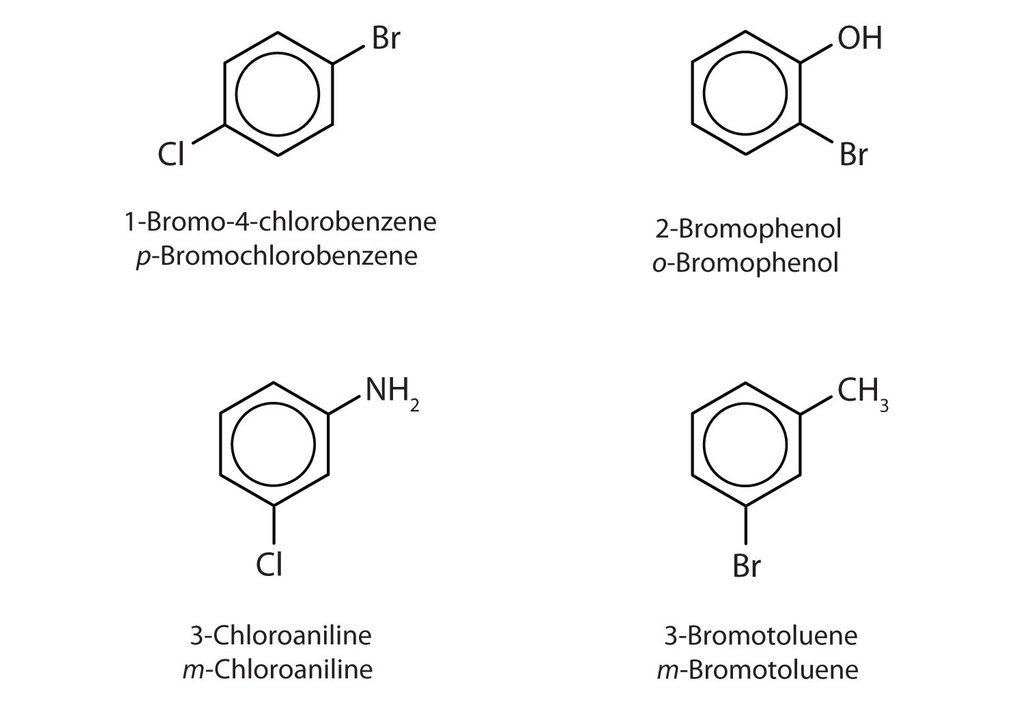
1. The simple aromatic ring containing six carbon atoms is considered benzene.
2. All other six-membered substituted structures are considered derivatives of benzene.
3. The six carbon atoms of the benzene ring is given as numbers from number 1 to 6.
4. The 1,4 position is called as para position.
5. The 2,6 position is called as ortho position.
6. The 3,5 position is called a meta position.
7. In the common name system the words ortho, para and meta are used.
8. In the IUPAC name system numbers 1 to 6 to which substituents are attached is used.
9. The substituents are numbered according to the priority order.
10. Example is shown in the diagram.
5
Distillation under reduced pressure
Vacuum distillation is a method of distillation whereby the pressure above the liquid mixture to be distilled is reduced to less than its vapor pressure (usually less than atmospheric pressure ) causing evaporation of the most volatile liquid(s) (those with the lowest boiling point). This distillation method works on the principle that boiling occurs when the vapor pressure of a liquid exceeds the ambient pressure. Vacuum distillation is used with or without heating the mixture.
Example : Petroleum products
6
Methods of purification
Steam distillation is a special type of distillation for temperature-sensitive materials like aromatic compounds. Many organic compounds tend to decompose at high sustained temperatures. Separation by distillation at the normal (1 atmosphere) boiling points is not an option, so water or steam is introduced into the distillation apparatus. The water vapour carries small amounts of the vaporized compounds to the condensation flask, where the condensed liquid phase separates, allowing for easy collection.
Example: Aromatic compounds.
7
Quantitative analysis
Analytical chemistry is the study of the separation, identification, and quantification of the chemical components of natural and artificial materials. In this, we used to find out qualitative as well as quantitative analysis of the compound.